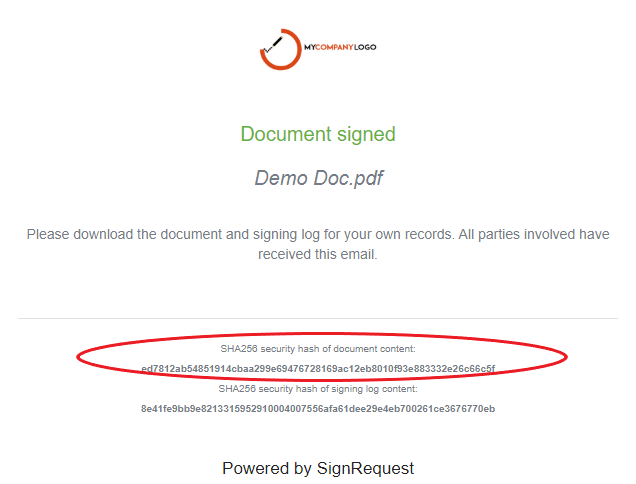
SignRequest uses 'SHA-256' cryptographic hash functions (hash codes, for short) to ensure the security of our electronically signed documents.
A cryptographic hash function is a mathematical algorithm that maps data of arbitrary size (often called the "message") to a bit string of a fixed size (the "hash value", "hash", or "message digest") and is a one-way function, that is, a function which is practically infeasible to invert.
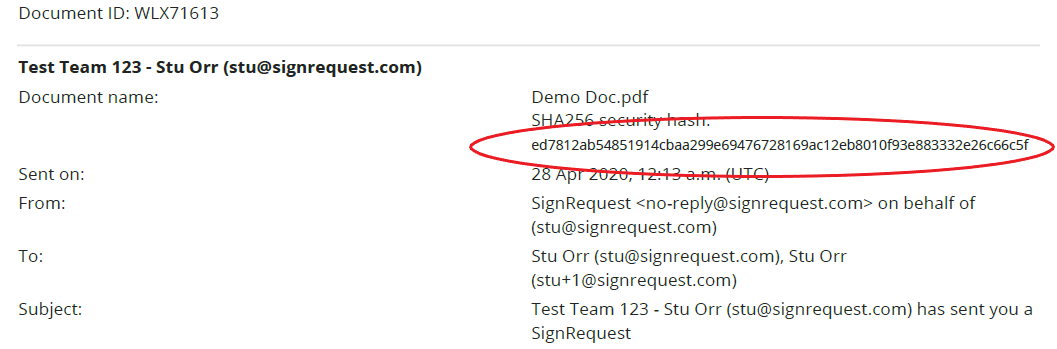
Hash codes are unique codes specific to an individual document. This is a great way to ensure that the document you are looking at is the original. Even if 1 pixel is changed in the document, this will result in a different code. The document that generates the hash code, that is visible in the SignRequest email and the signing log, will be the original document.
Signing Log
SignRequest 'Document Signed' email